![[field:title/]](/uploads/250702/2-250F21P612106.png)
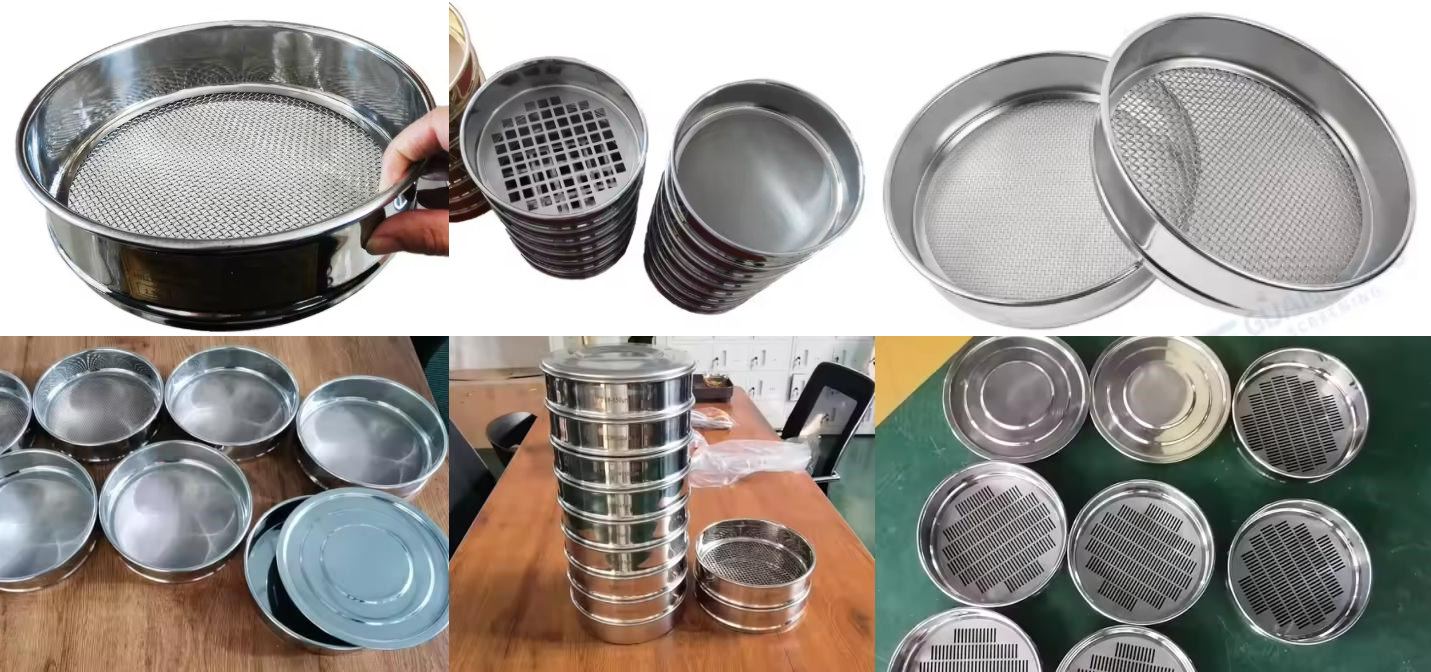
ASTM soil sieve is a standard test sieve for particle size analysis of soil samples manufactured according to the standards of the American Society for Testing and Materials. It is often used in engineering geology, civil engineering, agriculture and laboratory soil classification and research.
$100.00 - $980.00/Set
1. High standard accuracy
2. Strong durability of the sieve
3. Wide range of applications:from 75 mm to 20 μm
4. Flexible modular combination: A variety of sieve numbers can be freely combined and superimposed for use
Port:Any port in China (Mainland)or as you need.
About delivery:
| Quantity(sets) | 1-2 | >2 |
| Delivery time(days) | 5 | To be negotiated |
ASTM soil sieve refers to a soil particle size analysis tool manufactured in accordance with the standards published by the American Society for Testing and Materials, especially ASTM E11 "Standard Specification for Test Sieves and Screens", which is mainly used to grade and screen soil samples according to different particle sizes. It usually consists of a metal sieve frame and a woven metal screen with uniform and standardized sieve hole sizes and manufacturing tolerances to ensure the accuracy and repeatability of particle size analysis. ASTM soil sieve is a standard equipment for particle grading testing, soil classification and engineering suitability assessment in the fields of soil engineering, geotechnical analysis, and material testing.

ASTM standards are technical standards developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials to guide the testing and evaluation methods of materials, products, systems and services. Soil screening refers to the process of classifying soil samples by particle size through a set of standard sieves, mainly used to analyze the composition ratio of particles of different particle sizes in the soil.

ASTM E11: This is the main standard for test sieve specifications. It specifies the mesh size, wire diameter, sieve frame material and tolerances of woven wire screen cloth. This means that the mesh size, wire diameter, sieve frame material and manufacturing tolerances of the sieve must meet these strict requirements to ensure the accuracy and repeatability of the analysis results.
ASTM D6913: This standard covers the method of determining soil particle size distribution (gradation) by sieving analysis. It is used to separate particles into different particle size ranges and quantitatively determine the mass of particles in each range.
ASTM D1140: This standard involves the determination of the content of materials less than 75 microns (No. 200 sieve) in soil by water washing. Wet sieving is more effective than dry sieving to separate fine particles from large particles or soil aggregates.
|
ASTM Sieve No. |
Sieve Hole Size (mm) |
Sieve Hole Size (µm) |
ASTM Sieve No. |
Sieve Hole Size (mm) |
Sieve Hole Size (µm) |
|
3½ |
5.66mm |
5660µm |
4 |
4.75mm |
4750µm |
|
5 |
4.00mm |
4000µm |
6 |
3.35mm |
3350µm |
|
7 |
2.80mm |
2800µm |
8 |
2.36mm |
2360µm |
|
10 |
2.00mm |
2000µm |
12 |
1.70mm |
1700µm |
|
14 |
1.40mm |
1400µm |
16 |
1.18mm |
1180µm |
|
18 |
1.00mm |
1000µm |
20 |
0.850mm |
850µm |
|
25 |
0.710mm |
710µm |
30 |
0.600 mm |
600µm |
|
35 |
0.500mm |
500µm |
40 |
0.425mm |
425µm |
|
45 |
0.355mm |
355µm |
50 |
0.300mm |
300µm |
|
60 |
0.250mm |
250µm |
70 |
0.212mm |
212µm |
|
80 |
0.180mm |
180µm |
100 |
0.150mm |
150µm |
|
120 |
0.125mm |
125µm |
140 |
0.106mm |
106µm |
|
170 |
0.090 mm |
90µm |
200 |
0.075mm |
75µm |
|
230 |
0.063mm |
63µm |
270 |
0.053mm |
53µm |
|
325 |
0.045mm |
45µm |
400 |
0.038mm |
38µm |
|
450 |
0.032mm |
32µm |
500 |
0.025mm |
25µm |
|
635 |
0.020mm |
20µm |
|
|
|
ASTM standard sieve sizes can be either imperial or metric. Usually, sieve openings larger than 1/4 inch (6.3 mm) are expressed in imperial units, while finer sieves are expressed in "No.", representing the number of mesh holes per linear inch.
Soil particle size analysis using ASTM mesh test sieves is a classic dry or wet sieving method, suitable for coarse-grained soils with a particle size greater than 0.075mm (No.200), such as sand, gravel, etc.

Soil particle size analysis using ASTM test sieves is a standard method based on ASTMD6913 specification, suitable for coarse-grained soils such as sand and gravel with a particle size greater than 0.075mm. The test uses a set of sieves with ASTM standard mesh numbers (such as No.4, 10, 20, 40, 100, 200, etc.) to grade dry soil samples on a mechanical vibrating sieve. During operation, pour the pre-treated representative dry soil sample into the top layer of the sieve, arrange the sieves in order from large to small, and use vibration to cause particles of different particle sizes to pass through the sieve and remain in different sieve layers. After weighing the residues of each sieve layer and calculating the percentage, the particle size distribution curve and soil gradation characteristics can be obtained.
If the soil contains a certain proportion of fine particles (<0.075mm), the fine particle part needs to be analyzed in combination with the hydrometer method in ASTMD7928. This method is simple and has good repeatability. It is one of the most commonly used particle size testing methods in engineering, construction and geological surveys.
ASTM soil sieves work based on the physical separation and matching of particle size to the size of the sieve openings. Central to this process is the use of a series of test sieves that meet stringent standards. Use sieves of different mesh sizes to separate soil samples of mixed particle sizes according to the sieve mesh size. The particle size is separated layer by layer.
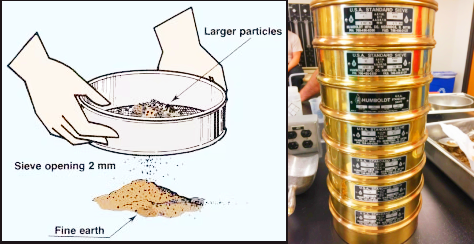
The specific process is: put the air-dried soil sample into the ASTM standard sieves stacked from coarse to fine, with the top layer being the largest aperture sieve and the bottom layer being the receiving tray. Through manual shaking or mechanical vibration by a vibrating sieve machine, the particles move in the sieve layer and pass through the sieve with an aperture larger than its own size, and finally remain on the sieve of the corresponding sieve number or on the bottom plate. The particles retained on each layer of the sieve represent a specific particle size range. By weighing the mass of each layer and calculating the percentage, the complete particle size distribution data can be obtained. This principle is applicable to dry or wet screening operations and is used for soil Basic methods for particle grading analysis.
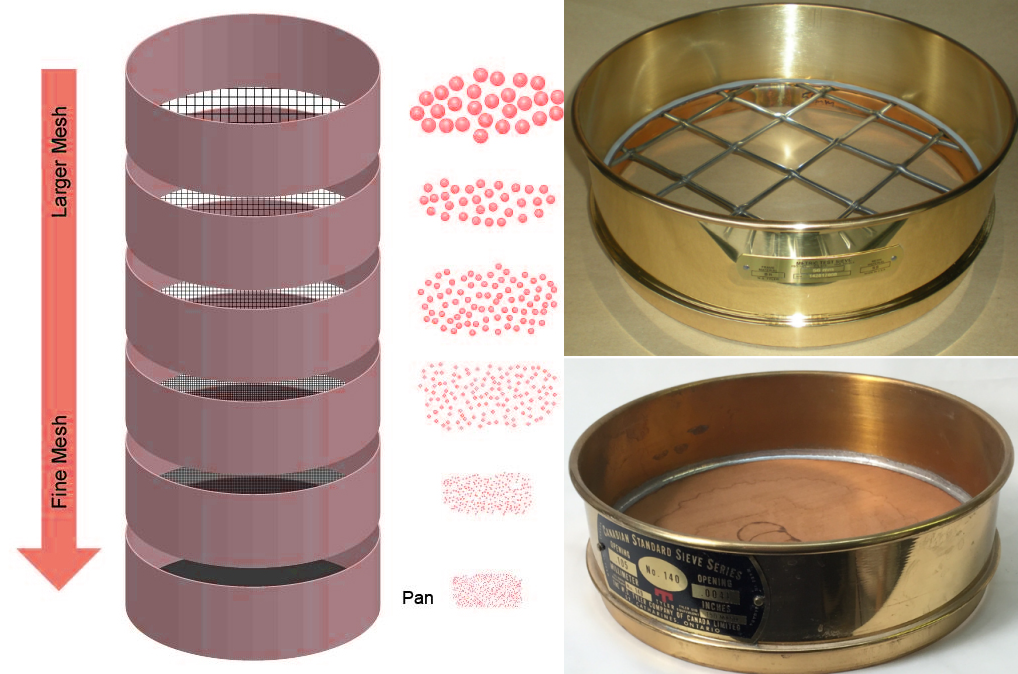
ASTM soil sieves play a vital role in the soil sieving process. Their main function is to accurately determine the particle size distribution of soil. By providing a standardized and accurate method to analyze the particle size composition of soil, they provide basic data and key information for various applications. Their main functions include accurate classification, ensuring data reliability, and guiding engineering applications.
Accurate classification: The mesh size of ASTM soil sieve is manufactured according to strict standards and has high precision. In the above sieving process, the soil particles can be accurately separated onto sieves of different apertures according to their size, so as to achieve accurate grading of soil particles, thereby providing a basis for subsequent data analysis.
Ensure data reliability: Due to its excellent material, such as corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant materials such as stainless steel, it is not easy to deform during the sieving process and can maintain the stability of the mesh size. Moreover, it complies with the relevant ASTM standards and has good versatility and interchangeability, so that when the same standard ASTM soil sieve is used for sieving experiments in different laboratories or different projects, the data obtained has high reliability and comparability, which is conducive to accurate evaluation of soil properties.
Guide engineering application: The soil particle distribution data obtained by ASTM soil sieve screening, combined with the particle size distribution curve, can help engineers determine the type of soil, such as gravel soil, sandy soil, silt or clay, and then evaluate the soil's bearing capacity, permeability, compressibility and other engineering properties, providing important reference for foundation selection and foundation treatment plan formulation in engineering design, ensuring the safety and stability of the project.
The structural composition of ASTM soil sieves is the basis for their accuracy and standardization. A typical ASTM test sieve is mainly composed of key components such as sieve frame, sieve mesh, sieve cover and sieve bottom.

The sieve frame is usually made of stainless steel or brass, with a diameter of 8 inches (203mm) or 12 inches (305mm)
The sieve mesh is woven metal mesh, manufactured according to the opening size specified in ASTME11
The sieve mesh aperture is commonly from 3" (75mm) to No.200 (75μm) or even finer (such as No.325)
The sieve cover and sieve bottom keep the sieve sample from leaking and collect the material under the sieve, which is often used for stacked screening
In agricultural soil improvement projects, technicians use ASTM soil sieve to analyze soil texture. First, collect The collected soil samples were air-dried, weeds, gravel and other debris were removed, and 500 grams of samples were placed on the top of the sieve group. The sieve group consists of sieves with mesh sizes of 4.75mm, 2.00mm, 0.425mm, 0.25mm, and 0.075mm from top to bottom, and a chassis is placed on the bottom to receive fine particles. The sieve group was installed on a vibrating screening machine and vibrated at a frequency of 150 rpm for 20 minutes to allow the soil particles to be fully screened.
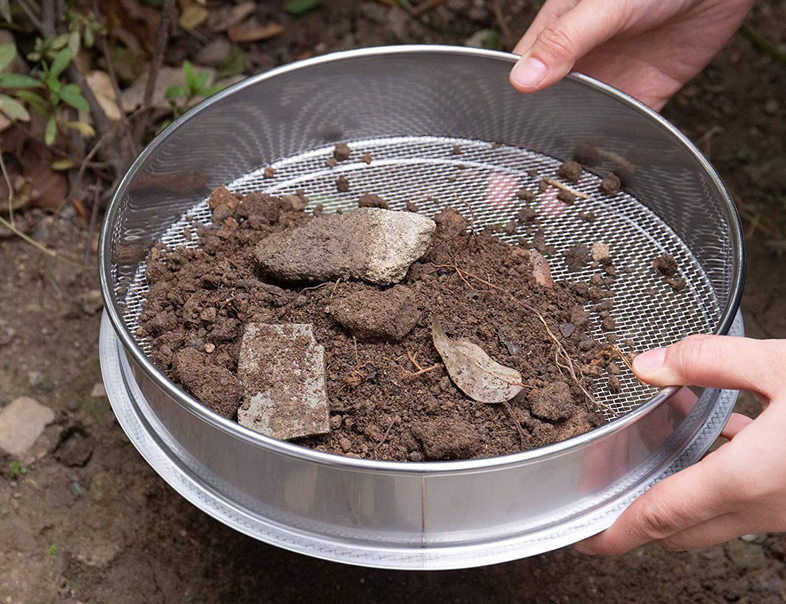

After the screening, the weight of the soil in each sieve layer and chassis was weighed separately, and the proportion of particles of different particle sizes was calculated. Through analysis, it was found that the soil 2-0.05 mm particles account for 65%, which is sandy loam with poor water and fertilizer retention capacity. Based on this, the project team formulated a plan to increase the application of organic fertilizer and add clay to improve the soil structure, which effectively improved the soil fertility.
Before the roadbed construction of the road project, the ASTM soil sieve is used to screen and test the soil in the soil borrowing area to determine whether its particle gradation meets the requirements of roadbed filling. If the content of fine particles is too high, the roadbed settlement problem is prone to occur during construction, and improvement measures such as sand mixing need to be taken. With its precise sieve hole specifications, the ASTM soil sieve provides accurate data support for soil property determination and engineering construction.

Soil engineering classification, feasibility assessment of earthwork construction
Prediction of foundation bearing capacity, screening of agricultural planting media
Academic and experimental research
ASTM soil sieves are widely used in many fields because of their standardization and accuracy. Engineers use sieving results to determine the gradation of soil to evaluate its bearing capacity, settlement characteristics and permeability, so as to design safe and stable building foundations. For example, knowing the particle size distribution of sand helps predict how compact it will be under load. When designing and building earth dams, embankments or retaining walls, the particle size distribution of fill soil needs to be precisely controlled.
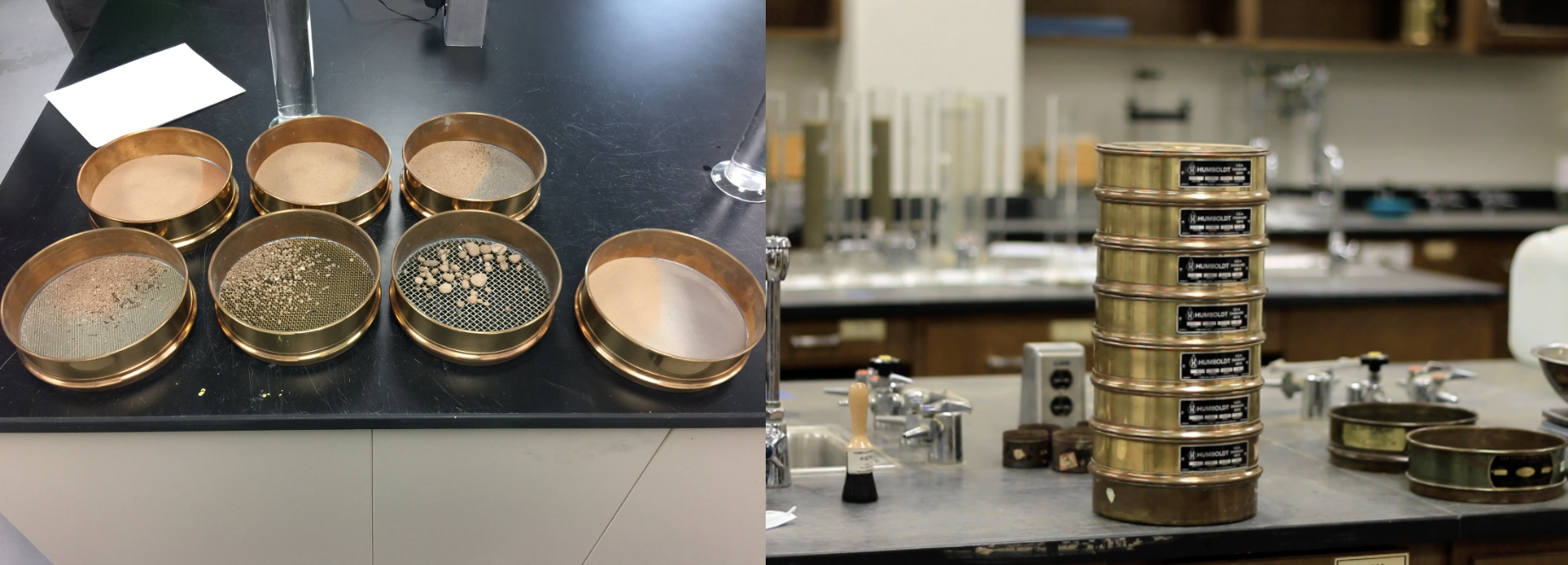

Soil particle size affects the rate at which contaminants are adsorbed, transported, and migrated through the soil. Sieve analysis helps predict how contaminants behave in different soil types. Geologists use sieve analysis to study the sources, transport processes, and depositional environments of river, lake, or marine sediments. Understanding the particle size distribution of an aquifer (a formation that stores groundwater) helps assess groundwater flow rates and the potential for contaminant dispersion.
When analyzing the particle size composition of backfill sand, a road construction laboratory used a set of ASTM standard sieves (No. 4 to No. 200) to separate the sand into coarse sand, fine sand, silt and other different particle sizes through dry screening to obtain the soil gradation curve. According to the screening results, it is judged whether the material meets the requirements of roadbed filling, such as whether the particle distribution is continuous and whether there is plastic silt inclusion, so as to guide the construction unit to adjust the batching plan.
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
Soil particle size analysis mainly uses sieving method (applicable to coarse-grained soil, such as gravel), sedimentation method (applicable to fine-grained soil, such as silt and c...
What is the price of electromagnetic screen vibrator
The price of electromagnetic sieve vibrators is affected by the model, power, control system, core component materials, etc., and is usually between $100 and $1,000. Simple models a...
Electromagnetic powder ultrasonic test sieve
Electromagnetic powder ultrasonic test sieve mesh covers 20-500 mesh, made of stainless steel, with ultrasonic system anti-blocking net, suitable for grading fine powders such as ap...
Silicon powder ultrasonic test sieve
Silicon powder ultrasonic test sieve is used to analyze the particle size of ultra-fine powders such as silicon powder that are easy to agglomerate or block the screen. It effective...
Are you interested?
![]()
Then we look forward to hearing from you
Contact Us
Industrials
Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road sitemap
