![[field:title/]](/uploads/250617/2-25061G61043528.png)
For laboratory sieves are commonly used tools in laboratories to screen, grade and separate granular materials of different particle sizes. The price range is between $30 and $500.
Diameter: 75mm/100mm/200mm/300mm
Sieve type: woven mesh (0.02mm-2.36mm)/perforated plate (1mm-125mm)/electroforming (75μm-5μm)
Sieving particle size: 0.025-3mm
Sieve material: stainless steel/brass/plastic
Number of layers: 1-7 layers
For laboratory sieves are precision instruments used for particle size analysis and screening of granular materials. They are mainly composed of stainless steel sieve frames and sieves, and have the characteristics of high precision and corrosion resistance. The sieves are divided into woven mesh, perforated plate or electroformed mesh, and the mesh size (mesh number) ranges from 3μm to 125mm. The larger the mesh number, the smaller the mesh size. For example, 200 mesh corresponds to about 74μm, which is suitable for fine powder screening; 10 mesh corresponds to about 2mm, which is suitable for coarse particles.

For Laboratory Sieves sieves usually adopt a multi-layer screening design, and can use multiple levels of sieves (2~7 layers) at the same time, arranged in order from large to small to achieve particle classification. Common diameters are 75mm, 200mm or 300mm, equipped with a vibrating screen machine or ultrasonic device to improve screening efficiency and reduce blockage. It is widely used in particle size detection and quality control in the fields of chemical, pharmaceutical, geological and other fields to ensure the accuracy and repeatability of experimental results.
Laboratory sieves are indispensable tools in particle size analysis. They separate particles of varying sizes using precise apertures, providing essential data for scientific research, quality control, and production processes. Sieves typically consist of a sturdy frame (usually stainless steel) and meshes of varying apertures. Common laboratory sieves include woven mesh, perforated plate, electroformed, and wet sieves, each with its own unique characteristics, suitable for different materials and analytical requirements.
1.Woven mesh screens
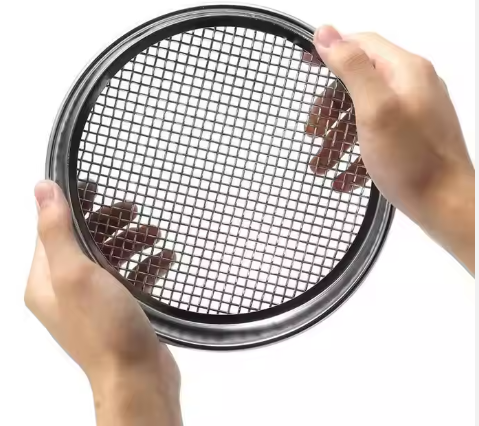

The screen is woven from fine metal wires (usually stainless steel) in a specific way to form a precise square or rectangular aperture.
The aperture range is 20μm (micrometer) or even smaller, to a coarse 125mm (millimeter) or larger, suitable for a variety of materials from powders to coarse particles.
Features: Suitable for most conventional dry screening and particle size analysis. With good aperture accuracy, it is widely used in almost all fields requiring particle size analysis, such as pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, construction, mining, agriculture, etc.
2.Perforated plate screen

The screen surface is made of a solid metal plate (usually stainless steel) through precision stamping or laser cutting to form round or square holes.
Aperture range: usually from about 1mm to 125mm or even larger.
Features: Especially suitable for handling heavier, abrasive or larger samples. The aperture is usually very precise and is common in the construction industry (aggregates, gravel, sand), mining (ores), agriculture (grains, seeds) and other fields that require screening of coarse particles.
3.Electroformed screen

The screen is manufactured by an electrodeposition process, where a metal layer is precisely deposited on a conductive substrate to form a mesh with ultra-high precision and uniformity. The aperture shape is usually round or square.
Pore size range: from 2μm to 150μm or even around 500μm
Features: The pore size is extremely precise and highly uniform, and it can provide very reliable and repeatable micro-particle analysis results. It is mainly used in high-end scientific research, precision chemicals, pharmaceuticals (active drug ingredients), electronic materials, ceramic powders and other fields that require extremely high-precision micro-particle analysis.
4.Wet screening
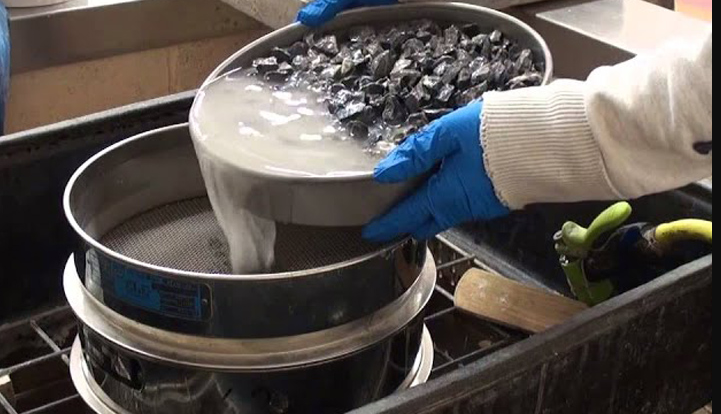

Usually based on woven mesh screens or perforated plate screens, it is designed for screening in the presence of water or other liquids
Features: When the sample contains sticky substances (such as clay, silt), or the particles are prone to agglomeration, dry screening may not be able to effectively separate. Wet screening can wash away the fine substances attached to the particles through the action of water flow, helping the particles to disperse and pass through the screen.
Application: Widely used in geological exploration, soil analysis, aggregate industry (cleaning sand and gravel), ceramic industry (removing clay), and certain food and chemical fields to separate and clean wet powders or particles.

|
Number |
Mesh (mm) |
Number |
Mesh (mm) |
Number |
Mesh (mm) |
Number |
Mesh (mm) |
|
2 |
13 |
26 |
0.71 |
90 |
0.16 |
260 |
0.06 |
|
3 |
6.5 |
28 |
0.63 |
100 |
0.154 |
280 |
0.055 |
|
4 |
5 |
30 |
0.6 |
110 |
0.14 |
300 |
0.054 |
|
5 |
4 |
32 |
0.55 |
115 |
0.13 |
320 |
0.048 |
|
6 |
3 .2 |
36 |
0.5 |
120 |
0.125 |
325 |
0.045 |
|
7 |
2.8 |
40 |
0.45 |
130 |
0.111 |
350 |
0.041 |
|
8 |
2.5 |
45 |
0.4 |
140 |
0.105 |
360 |
0.4 |
|
9 |
2.2 |
50 |
0.355 |
150 |
0.1 |
400 |
0.0385 |
|
10 |
2 |
55 |
0.315 |
160 |
0.098 |
500 |
0.03 |
|
12 |
1.6 |
60 |
0.3 |
180 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
14 |
1.43 |
65 |
0.25 |
190 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
16 |
1.25 |
70 |
0.22 |
200 |
0.075 |
|
|
|
18 |
1 |
75 |
0.2 |
220 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
20 |
0.9 |
80 |
0.18 |
240 |
0.065 |
|
|
|
24 |
0.8 |
85 |
0.17 |
250 |
0.063 |
|
|
|
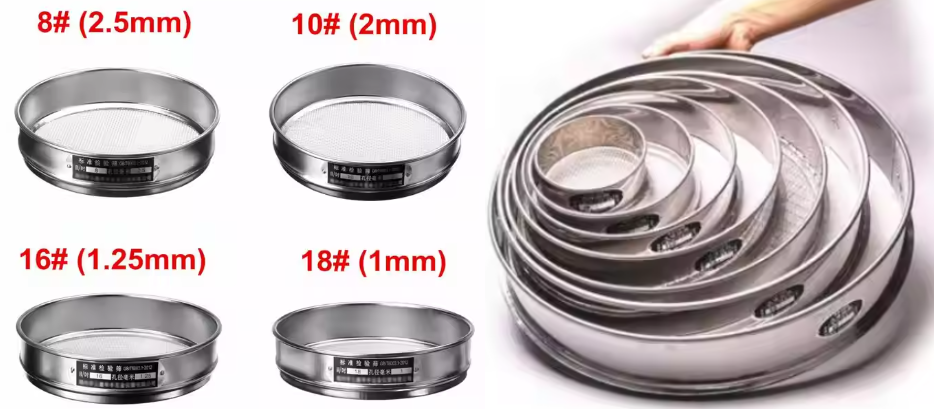
Specifications of stainless steel sample sieves. If you need special specifications, please contact online customer service for consultation. |
|||||||
| ASTM E11 | ISO 565/3310-1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Alternate | Size |
| 100.0mm | 4in | - |
| 90.0mm | 3 1/2in | - |
| 75.0mm | 3in | - |
| 63.0mm | 2 1/2in | 63.0mm |
| - | - | 56.0mm |
| 53.0mm | 2.12in | 53.0mm |
| 50.0mm | 2in | 50.0mm |
| 45.0mm | 1 3/4in | 45.0mm |
| - | - | 40.0mm |
| 37.5mm | 1 1/2in | 37.5mm |
| - | - | 35.5mm |
| 31.5mm | 1 1/4in | 31.5mm |
| - | - | 28.0mm |
| 26.5mm | 1.06in | 26.5mm |
| 25.0mm | 1in | 25.0mm |
| 22.4mm | 7/8in | 22.4mm |
| - | - | 20.0mm |
| 19.0mm | 3/4in | 19.0mm |
| 18.0mm | - | 18.0mm |
| 16.0mm | 5/8in | 16.0mm |
| - | - | 14.0mm |
| 13.2mm | 0.530in | 13.2mm |
| 12.5mm | 1/2in | 12.5mm |
| 11.2mm | 7/16in | 11.2mm |
| - | - | 10.0mm |
| 9.5mm | 3/8in | 9.5mm |
| - | - | 9.0mm |
| 8.0mm | 5/16in | 8.0mm |
| - | - | 7.1mm |
| 6.7mm | 0.265in | 6.7mm |
| 6.3mm | 1/4in | 6.3mm |
| 5.6mm | No. 3 1/2 | 5.6mm |
| - | - | 5.0mm |
| 4.75mm | No.4 | 4.75mm |
| - | - | 4.50mm |
| 4.00mm | No.5 | 4.00mm |
| 3.55mm | - | 3.55mm |
| 3.35mm | No.6 | 3.35mm |
| - | 1/8in* | - |
| 3.15mm | - | 3.15mm |
| 2.80mm | No.7 | 2.80mm |
| - | - | 2.50mm |
| 2.36mm | No.8 | 2.36mm |
| 2.00mm | No.10 | 2.00mm |
| - | - | 1.80mm |
| 1.70mm | No.12 | 1.70mm |
| - | - | 1.60mm |
| 1.40mm | No.14 | 1.40mm |
| - | - | 1.25mm |
| 1.18mm | No.16 | 1.18mm |
| - | - | 1.12mm |
| 1.00mm | No.18 | 1.00mm |
| - | - | 900µm |
| 850μm | No.20 | 850µm |
| - | - | 800µm |
| 710μm | No.25 | 710µm |
| - | - | 630µm |
| 600μm | No.30 | 600µm |
| - | - | 560µm |
| 500μm | No.35 | 500µm |
| - | - | 450µm |
| 425μm | No.40 | 425µm |
| - | - | 400µm |
| 355μm | No.45 | 355µm |
| - | - | 315µm |
| 300μm | No.50 | 300µm |
| - | - | 280µm |
| 250μm | No.60 | 250µm |
| - | - | 224µm |
| 212μm | No.70 | 212µm |
| - | - | 200µm |
| 180μm | No.80 | 180µm |
| - | - | 160µm |
| 150μm | No.100 | 150µm |
| - | - | 140µm |
| 125μm | No.120 | 125µm |
| - | - | 112µm |
| 106μm | No.140 | 106µm |
| - | - | 100µm |
| 90μm | No.170 | 90µm |
| - | - | 80µm |
| 75μm | No.200 | 75µm |
| - | - | 71µm |
| 63μm | No.230 | 63µm |
| - | - | 56µm |
| 53μm | No.270 | 53µm |
| - | - | 50µm |
| 45μm | No.325 | 45µm |
| - | - | 40µm |
| 38μm | No.400 | 38µm |
| - | - | 36µm |
| 32µm | No.450 | 32µm |
| 25µm | No.500 | 25µm |
| 20µm | No.635 | 20µm |
|
Type |
Mesh size range |
Main purpose |
Advantages |
|
Woven mesh sieve |
20μm-several millimeters |
Dry fine particle screening |
Low cost, uniform mesh |
|
Perforated plate sieve |
1mm-125mm |
Coarse particle screening |
Durable and suitable for heavy loads |
|
Electroforming sieve |
3μm-100μm |
Ultrafine powder high-precision screening |
High precision, consistent mesh |
|
Wet sieve |
10μm-several millimeters |
Wet or sticky material screening |
Suitable for wet materials, reduce clogging |
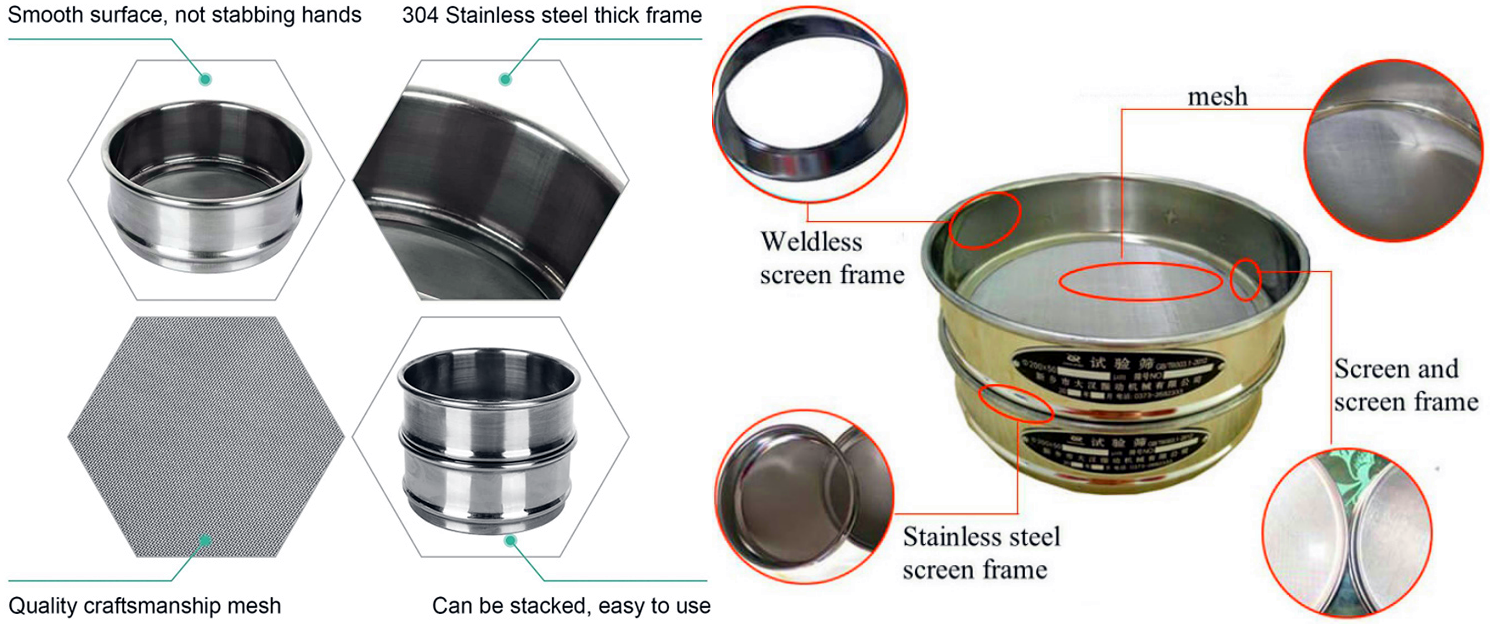
The laboratory sieving process usually involves stacking a series of sieves of different apertures in descending order to form a sieving hierarchy. The sample is placed on the top sieve, and then the particles are forced down through each layer of the sieve by mechanical vibration (using a sieving machine). In this way, particles of different sizes are separated and retained on the corresponding sieves, thereby achieving an accurate analysis of the sample particle size distribution.
The aperture range of sieves is very wide, ranging from very large sizes to very fine sizes depending on different application requirements and manufacturing standards.

Large aperture: ranging from 4.75 mm (approximately equivalent to 4 mesh) to 2.00 mm (10 mesh), suitable for screening larger particles.
Medium aperture: ranging from 1.00 mm (18 mesh) to 0.250 mm (60 mesh), commonly used for general powder and granular material classification.
Small aperture: from 0.150 mm (100 mesh) to 0.038 mm (400 mesh), this type of sieve is suitable for finer material screening.
Micro aperture: less than 0.038 mm, such as 0.025 mm or smaller, can even reach a few microns (μm), this level of sieve is usually used for particularly fine material analysis.

For labratory sieves are widely used in particle size analysis and material classification in many industries. With their high precision and multi-layer screening characteristics, they play a key role in scientific research and quality control. In the pharmaceutical industry, sieves are used to screen drug powders to ensure uniform particle size (such as 200 mesh to screen particles below 74μm) and optimize drug efficacy and solubility; in geological research, multi-layer sieves (10 mesh to 100 mesh) are used to analyze the particle size distribution of soil or ore and judge geological characteristics; in the food industry, sieves are used to detect the fineness of raw materials such as flour and powdered sugar and remove impurities.
In the chemical industry, catalyst or pigment particles are screened (such as using a 20μm electroforming sieve) to ensure reaction efficiency or coating quality; in the environmental protection field, wet screening is used to analyze suspended particles in sewage treatment and evaluate water quality. For laboratory sieves sieves are usually equipped with vibration or ultrasonic devices, combined with 2 to 7 layers of sieves, to achieve grading from coarse particles to ultrafine powders, meeting the precise needs of different scenarios.
For Laboratory Sieves, often referred to as test sieves or standard test sieves, are fundamental tools in particle analysis. With precisely controlled mesh sizes, they effectively separate powders and granular materials to determine the sample's particle size distribution. Whether used for scientific research, product quality control, or production process optimization, For Laboratory Sieves provide accurate and reproducible particle size data.
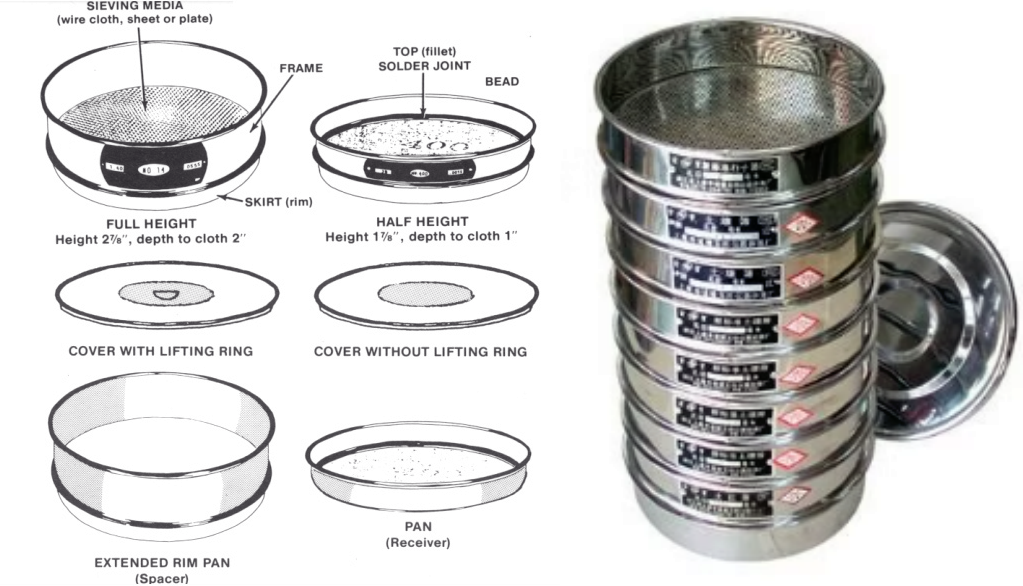

Through sieves with different mesh sizes, the material is graded according to the particle size and the particle size distribution is determined. It is often used for quality control and research. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to analyze the size distribution of drug particles to optimize the drug absorption characteristics.
Remove impurities or particles that do not meet the specifications in the material to ensure the purity of the sample. It is suitable for chemical, food, pharmaceutical and other industries.
Divide the material into different particle size segments (such as 2~7 particle segments) for material property analysis in geology, metallurgy, building materials and other fields.
In the field of laboratory sieve supply, Xinxiang Dahan Machinery Co., Ltd. is one of the more common equipment manufacturers in China, providing a variety of standard laboratory sieves and supporting equipment.
These laboratory sieving equipment usually have precise mesh sizes to meet various needs from rough screening to fine analysis. In addition, Dahan Machinery may also provide sieves that meet international standards (such as ISO, ASTM, etc.) to ensure the accuracy and repeatability of experimental results.
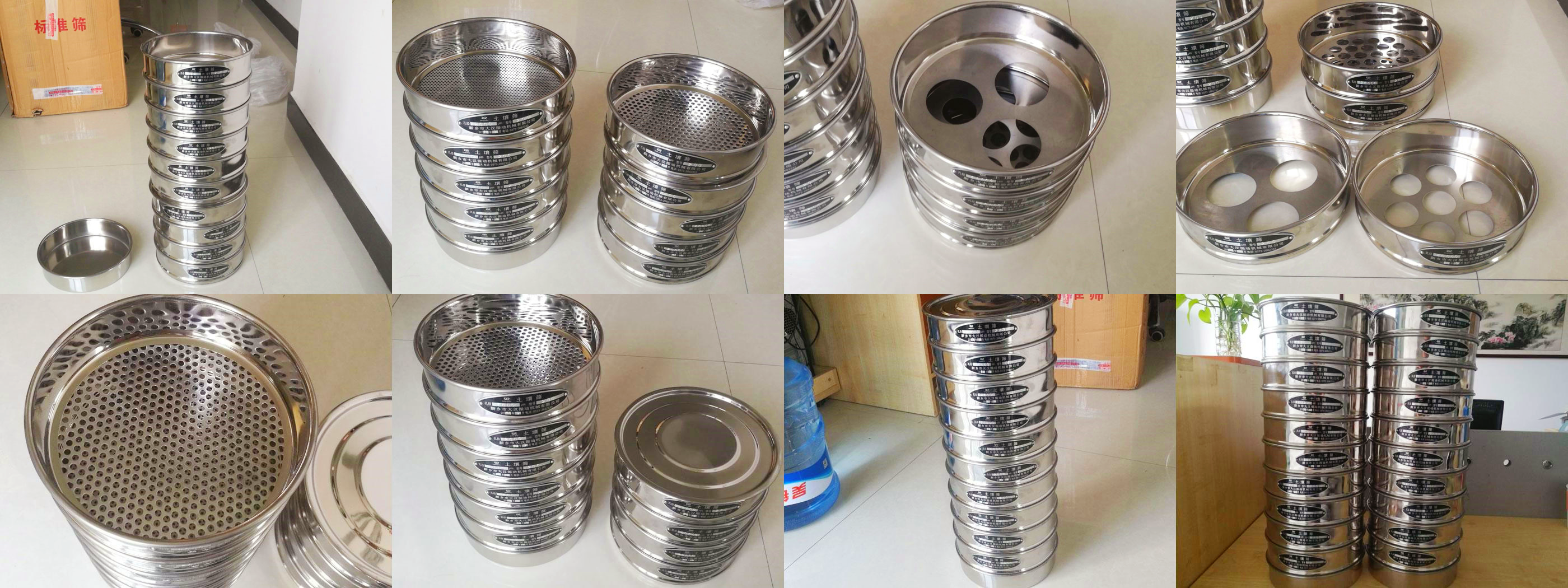

If you need to contact Dahan Machinery for more information about laboratory sieves, including product catalogs, quotes or technical support, it is recommended to contact customer service directly. This will provide the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Test Analysis Sieve is a sieve for separating mixtures. It mainly makes the mixture of particles of different...
Sieve Analysis Test is mainly used for grading the particle size composition of various powder materials,...
Soil Test Sieve can be used for soil grading, screening, analysis, testing, filtering various soils, widely used...
Standard Sieves standard sieve is a tool for particle size classification and particle size detection of material...
For laboratory sieves are commonly used tools in laboratories to screen, grade and separate granular materials ...
size sieve for soil is made of stainless steel and can sieve out dust and soil. The fine sieve sizes are 0.075mm and 2mm, and the coarse sieve sizes are 4.75mm, 25mm, and 75mm.......
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils is used to determine the weight proportions of different particle sizes, such as sand, silt, and clay, in a given soil sampl...
Agricultural soil testing sieve
Agricultural soil testing sieve uses a 2mm sieve to separate the fine particles in the soil in order to analyze its physical properties and nutrient content.......
Stainless steel soil sieve is called soil sieving instrument or soil analysis sieve, and the mesh size of the sieve is between 10 mesh and 200 mesh.......
Are you interested?
![]()
Then we look forward to hearing from you
Contact Us
Industrials
Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road sitemap
