Thursday July-17 2025 17:01:03
Geotechnical soil sieve are usually composed of multiple layers, usually including 8 to 12 layers or even more sieves with different mesh sizes. The mesh size of each layer ranges from a coarse sieve of a few meshes to a fine sieve of several hundred meshes, which can finely grade soil samples. It is mainly suitable for particle size analysis of powdery, granular and small bulk materials. This type of equipment is mainly divided into stainless steel sieves and brass sieves according to its material and structure. The common sieve frame is a circular structure, which is convenient for stacking. In terms of sieve hole size, Geotechnical soil sieve covers coarse sieves from tens of millimeters to fine sieves of 0.075 mm (200 mesh), which can accurately distinguish components of different particle sizes such as gravel, sand, and silt.
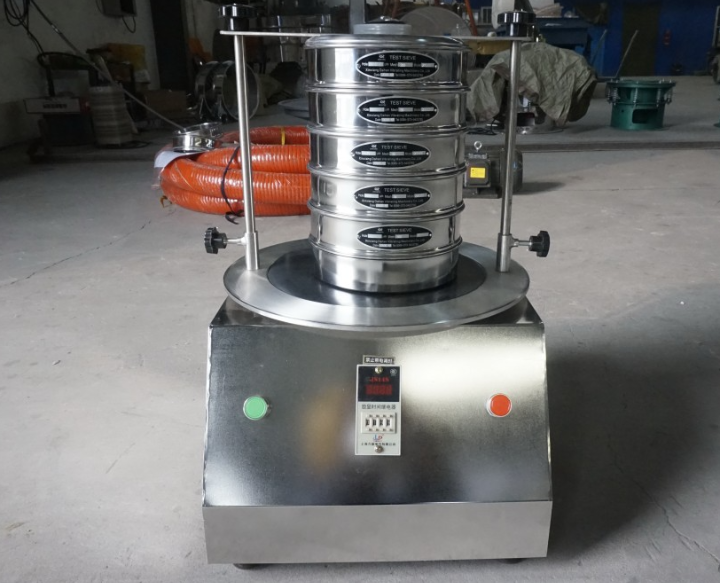

Geotechnical soil sieve is mainly used for particle size analysis and classification of soil particles in geotechnical tests. Its classification method is usually based on sieve hole size, sieve material, structural form and the standard system followed.
Classification by sieve hole size and purpose
In geotechnical tests, the commonly used standard sieve hole size is to divide soil components according to a specific particle size range.
Coarse-grained soil sieve (gravel and coarse sand sieve): usually refers to sieves with mesh size greater than or equal to 4.75 mm (No. 4 sieve). These sieves are used to separate larger particles such as gravel and coarse sand in the soil.
Fine-grained soil sieve (fine sand and silt sieve): mainly refers to sieves with mesh size between 4.75 mm (No. 4 sieve) and 0.075 mm (No. 200 sieve). Used to separate fine sand and some silt in the soil.
Fine-grained soil sieve (clay and fine particle sieve): sieves with mesh size less than 0.075 mm (No. 200 sieve). For particles passing through the 0.075 mm sieve, more sophisticated methods such as the density meter method or the pipette method are usually required for further analysis.
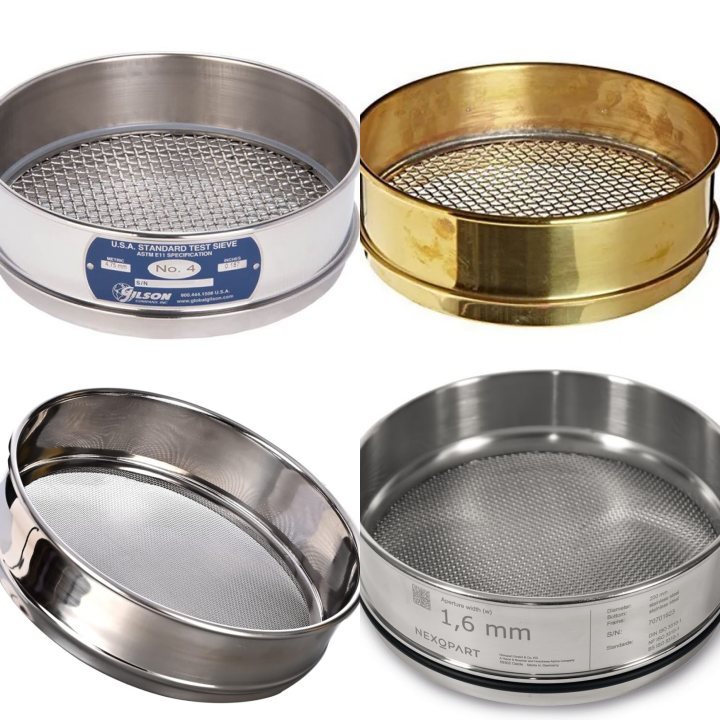
Classification by sieve material
The material selection of the sieve directly affects the durability, corrosion resistance and stability of the mesh size of the sieve, which in turn affects the accuracy of the test results.
Stainless steel sieve: This is the most commonly used material for Geotechnical soil sieves. Stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance, high strength and good wear resistance. These characteristics ensure that the sieve holes are not easily deformed during long-term use, thereby ensuring the screening accuracy and the service life of the sieve. Stainless steel sieves are suitable for routine geotechnical tests in laboratories and on-site, and can withstand the influence of different humidity and chemical environments.
Brass sieves: Brass sieves have certain flexibility, but are generally not as good as stainless steel in terms of wear resistance and corrosion resistance. They may still be used in some occasions where wear and corrosion requirements are not high.

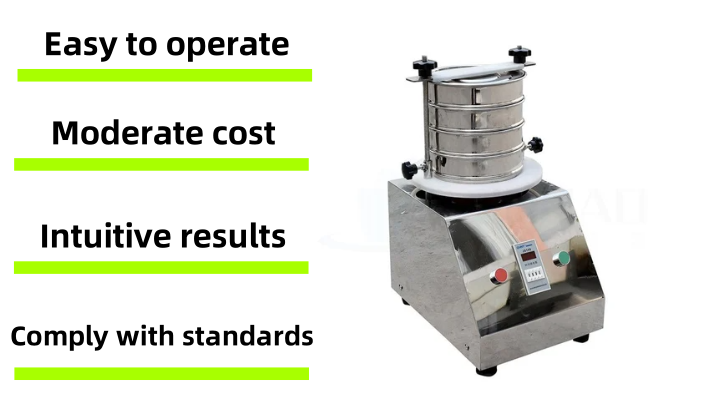
Geotechnical soil sieve has some obvious advantages in geotechnical testing and related fields, making it an irreplaceable tool for particle size analysis. Its advantages include easy operation, moderate cost, intuitive results and compliance with standard specifications. The following are its main advantages:
Basic tool for particle size analysis: Soil sieving is the basic method for determining the particle size composition of soil. Through a series of Geotechnical soil sieves with different sieve hole sizes, soil samples can be separated into components of different particle sizes, thereby obtaining the particle size distribution curve of the soil. This is a key step in classifying soil, evaluating its engineering properties (such as permeability, shear strength, etc.), and guiding engineering design (such as roadbed, foundation, filter layer design).
Easy to operate and relatively low cost: The operation process of Geotechnical soil sieve is usually intuitive. Whether it is manual sieving or with an electric vibrating sieve machine, its operation is relatively simple and does not require complex expertise or long-term training. Compared with some high-precision particle size analysis instruments (such as laser particle size analyzers), the purchase and maintenance costs of soil sieves are significantly lower, making them widely used in various laboratories and field tests.
The results are intuitive and easy to understand: The sieving results can be directly calculated by the mass of the residue at each level, and the obtained particle size distribution curve is intuitive and clear, which is easy for engineers and technicians to understand and apply. This direct physical separation method makes the results highly reliable and repeatable, and it is convenient for results to be compared between different laboratories.
Applicable to a variety of soil types: Geotechnical soil sieve can handle a variety of soil samples, including coarse-grained soils (such as gravel, sand) and some fine-grained soils (such as silt). Although other analytical methods are required for finer clay particles, sieving can provide sufficiently accurate particle size data for sand and gravel soils commonly found in engineering.
Preliminary on-site analysis: In some cases, a simple Geotechnical soil sieve kit can be used to perform preliminary particle size analysis on site, providing immediate reference for engineering decisions. Although not as accurate as laboratory results, it is practical in emergency situations or preliminary surveys.
| No. | Type | Mesh(mm) | No. | Type | Mesh(mm) |
| 1 | 8# | 2.360 | 15 | 70# | 0.212 |
| 2 | 10# | 2.000 | 16 | 80# | 0.180 |
| 3 | 12# | 1.700 | 17 | 100# | 0.150 |
| 4 | 14# | 1.400 | 18 | 120# | 0.125 |
| 5 | 16# | 1.180 | 19 | 140# | 0.106 |
| 6 | 18# | 1.000 | 20 | 170# | 0.09 |
| 7 | 20# | 0.850 | 21 | 200# | 0.075 |
| 8 | 25# | 0.710 | 22 | 230# | 0.063 |
| 9 | 30# | 0.600 | 23 | 270# | 0.053 |
| 10 | 35# | 0.500 | 24 | 325# | 0.045 |
| 11 | 40# | 0.425 | 25 | 400# | 0.038 |
| 12 | 45# | 0.355 | 26 | 500# | 0.028 |
| 13 | 50# | 0.300 | 27 | >500# | <0.028 |
| 14 | 60# | 0.250 |
The main uses of Geotechnical soil sieve focus on obtaining and analyzing soil particle size composition information. This is essential for understanding and evaluating the physical properties of various bulk granular materials. Specifically, its applications are reflected in the following aspects:
Particle size distribution determination: Geotechnical soil sieve can separate the sample to be tested into particle components of different sizes through a series of sieves with different apertures. This allows researchers and engineers to draw particle size distribution curves to quantify the percentage content of particles in different size ranges.
Material property evaluation: Particle size distribution data is the basis for evaluating key engineering properties of bulk materials. For example, it can help predict the permeability, density, shear strength and stability of materials, which is essential for various engineering designs.
Quality control and material screening: Geotechnical soil sieve is used to verify whether materials meet specific particle size specifications during material production, procurement and use. For example, when preparing mixed materials, ensure that the particle size of each component meets the design standard to ensure the performance and consistency of the final product.
Mixing and grading optimization: Through the sieving analysis of single or multiple components, the grading ratio of multiple granular materials can be optimized to achieve ideal performance, such as achieving higher density or a specific permeability coefficient.
Pollutant migration research: In the field of environmental science, understanding the particle size distribution of soil or sediment helps to study the adsorption and migration behavior of pollutants in particles of different particle sizes, and provide data support for environmental remediation plans.
In general, Geotechnical soil sieve is a basic tool for understanding and controlling the physical properties of various granular materials, providing necessary data support for material scientific research, engineering design, construction and quality control.
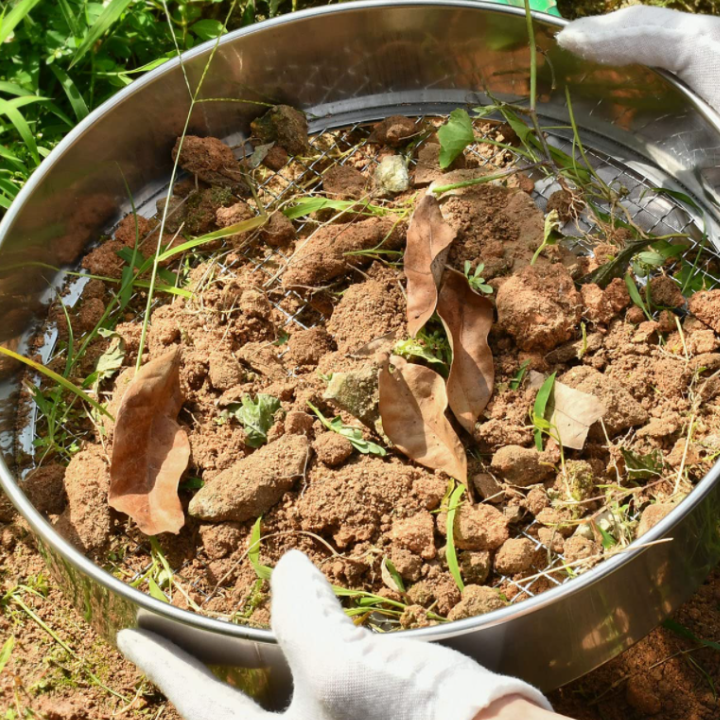

The main purpose of Geotechnical soil sieve is to perform soil particle size analysis, which is a basic test in the field of civil engineering and geological exploration. Through sieving, the relative content of particles of different particle sizes (such as gravel, sand, and silt) in the soil sample can be determined, thereby obtaining information on the particle size distribution of the soil. This data is essential for understanding the physical properties of soil and predicting its engineering behavior. In construction and infrastructure projects, Geotechnical soil sieve is used to evaluate the suitability of foundation soil. By analyzing the particle size distribution of the soil, it can be determined whether the soil is suitable as a foundation for structures such as buildings, roads, and bridges. In the construction of transportation projects such as highways, railways, and airport runways, Geotechnical soil sieve is used to control the quality of roadbed fillers and pavement aggregates (such as crushed stone and sand). Through sieving, it can be ensured that the selected aggregate particle size meets the design specification requirements to ensure the stability of the roadbed and the durability and skid resistance of the pavement. In projects that require water flow control, such as dams, reservoirs, drainage systems, landfills, etc., Geotechnical soil sieve is used to design and verify the particle size distribution of filter layers, drainage layers, and filter layers. A suitable filter layer can prevent fine particles from being carried away by water flow, causing pipe blockage or foundation instability, while ensuring smooth water infiltration. For soils that need to be improved (such as soft soil, expansive soil, collapsible loess, etc.), Geotechnical soil sieve can be used to monitor and evaluate the particle size changes after the amendment (such as lime, cement, fly ash) is mixed with the soil, as well as the gradation characteristics of the improved soil, so as to optimize the improvement plan. Geotechnical soil sieve also has its applications in agricultural science. It can be used to analyze the physical structure of farmland soil, understand the impact of soil particle distribution on soil aeration, water retention, fertility, and the growth environment of plant roots, and thus guide soil management and improvement measures in agricultural production. In summary, Geotechnical soil sieve provides important data support for the design, construction, quality control and research of various engineering projects by providing accurate soil particle size distribution information.
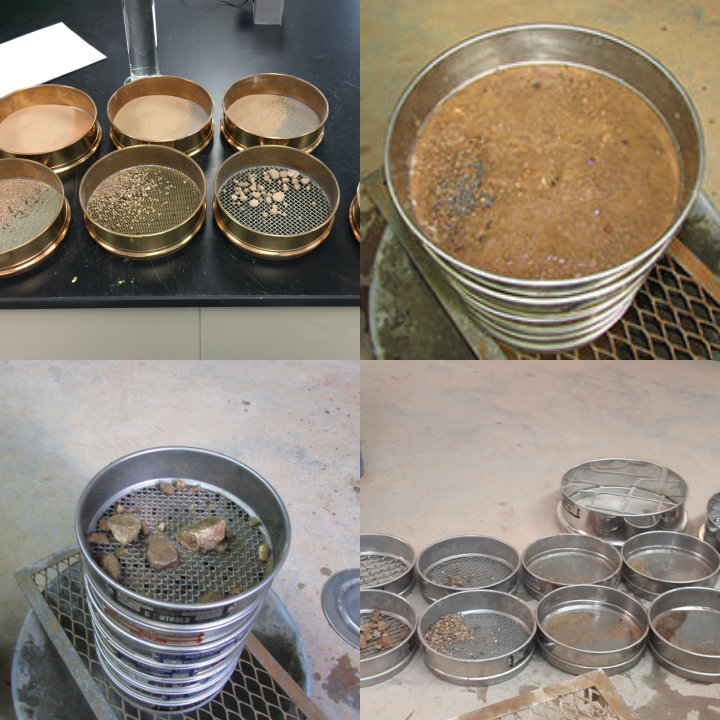

Geotechnical soil sieve is a commonly used tool in geotechnical tests. Its operating principle is to use the difference in sieve hole size to physically separate soil particles. The device consists of main components such as sieve frame and sieve mesh, and achieves effective passage or interception of particles through vibration or shaking. Its advantage is that the operation process is relatively direct, without the need for complex equipment operation, so that different users can perform particle size analysis relatively easily. At the same time, the sieving results are presented in the form of sieve residues at various levels. The data is intuitive, easy to understand and calculate, and provides a direct basis for subsequent engineering judgments.
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
Size analysis of soils is a standard laboratory procedure used to determine the proportion by weight of different particle sizes (like sand, silt, and clay) within a given soil samp...
Quartz sand ultrasonic slap sieve
Quartz sand ultrasonic slap sieve is a particle size analysis device that combines ultrasonic technology with the vibration principle of the slap sieve. It is mainly used for high-p...
Powder test sieve is a laboratory device that physically separates powder samples according to particle size by precisely controlling vibration and using multiple layers of standard...
Water Test Sieve is a method of particle size analysis using water flow as a medium. It is mainly used to deal with ultrafine powders and particles that are easy to agglomerate, hig...
Application sand Specifications of Agricultural Soil Test Sieves
The agricultural soil test sieve is a screening device for accurately grading soil particles, which is widely used in agricultural soil analysis and quality assessment. It quickly s...
Jul 17, 2025
As a basic tool in geotechnical tests, the core function of geotechnical soil sieve is to analyze the...
Jul 16, 2025
Electromagnetic powder ultrasonic test sieve
Electromagnetic powder ultrasonic test sieve combines traditional mechanical vibration with high-freq...
Jul 15, 2025
Powder test sieve is a laboratory device that physically separates powder samples according to partic...
Jul 14, 2025
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
Size analysis of soils is a standard laboratory procedure used to determine the proportion by weight ...
![]()
Then we look forward to hearing from you
Contact Us
Industrials
Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road sitemap
