![[field:title/]](/uploads/250401/2-25040109445UM.jpg)
Sieve analysis is the process of grading particulate materials by size through a sieve. It is a traditional and commonly used particle size analysis method, especially suitable for particulate materials with a large particle size range.
Size: 1 micron-2000 micron
Screening particle size: 0.038-3mm
Material: SUS304, SS316 stainless steel, brass or customized
Features
1. Accurate screening, can screen 0.025~3mm.
2. The test screen box and vibration plate are made of stainless steel, and the screen frame is made of polished stainless steel with a wall thickness of 0.6 mm. It is non-magnetic and can withstand high temperatures below 300°C.
3. The screen and the screen frame are fixed by soldering and will not loosen or shake.
4. It can be automatically shut down at a fixed time to ensure experimental repeatability.
Sieve analysisinvolves sequentially sieving a sample through a set of standard sieves with different aperture sizes, measuring the mass of the residue on each sieve, and thus determining the percentage of particles of different sizes in the material. Sieve aperture sizes include 100 mm, 63 mm, 50 mm, 31.5 mm, 25 mm, 16 mm, 10 mm, 2.0 mm, 0.5 mm, 0.125 mm, and 0.063 mm, among others. Sieve methods can be broadly classified into two categories: dry sieves, used for dry, free-flowing particles, and wet sieves, which require water dispersion and are suitable for moist or easily agglomerated fine particles.

Sieve analysis is a process used to assess the particle size distribution of granular materials like sand, gravel, soil, and other aggregates. This analysis helps in determining the particle size distribution of the material and is crucial in various fields such as construction, geotechnical engineering, and material science.
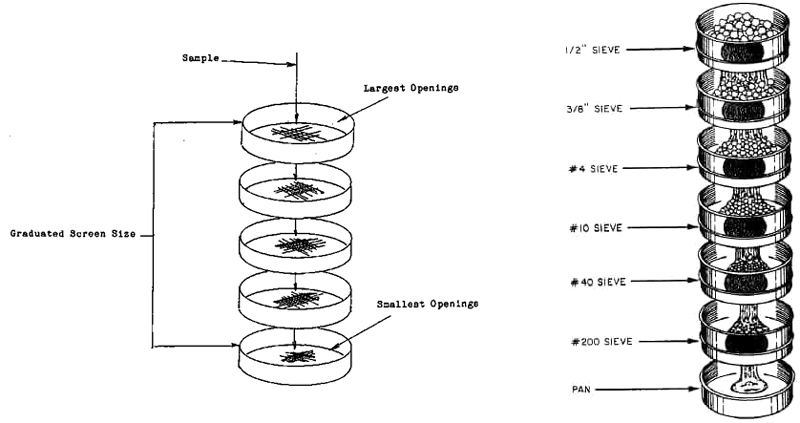
The material to be tested is poured onto a set of sieves with gradually decreasing mesh sizes, and the material is forced through the meshes by vibration or other means. Particles larger than the mesh are retained on the sieves, while particles smaller than the mesh pass through the mesh and fall into the next layer of sieves. By measuring the mass of the material retained on each layer of sieves, the particle size distribution of the material can be obtained.

Sieve analysis is used for quality control of materials such as cement and food to ensure that products meet specified particle size requirements; it also involves understanding the particle size distribution of materials through sieve analysis, providing data support for new product development; optimizing production processes to improve product performance; studying the particle size composition of materials such as soil, rock, and minerals, and providing data for geological and soil science research; and analyzing particulate matter in air, water, and soil to assess environmental quality.

Particle size distribution refers to the measurement and description of the percentage distribution of particles of different sizes in a granular material in a sieving analysis. Through sieving analysis, the proportion of particles in each size range in the material can be determined, thereby obtaining a particle size distribution curve or table.
Particle size distribution is usually presented in the following ways:
Cumulative passing curve: This is one of the most common forms of particle size distribution. The horizontal axis of the curve represents the particle size (usually expressed in sieve hole size), and the vertical axis represents the percentage of particles passing through the sieve hole of that size. The curve starts from the lower left and gradually rises to the upper right, representing a gradual increase in the percentage of smaller particles.
Cumulative retention curve: This is another common form of particle size distribution. The horizontal axis of the curve represents the particle size, and the vertical axis represents the percentage of particles retained on the sieve hole of that size. The curve usually starts from the upper left corner and gradually decreases to the lower right, representing a gradual decrease in the percentage of smaller particles.
Particle size distribution table: In addition to the curve, the particle size distribution can also be presented in a table, which lists the aperture size of each sieve hole and the percentage of particles passed and retained.
① Classification by screen material
| Classification basis | Type | Features | Picture |
| Wire mesh screen | Woven from stainless steel, brass and other metal wires, high strength and good wear resistance | Suitable for most granular materials, such as ore, coal, sand and gravel, etc. |
 |
| Perforated plate screen | Pressing from metal plates, precise aperture and high strength | Suitable for large particles or highly abrasive materials, such as gravel, slag, etc. |
 |
| Nylon screen | Woven from nylon wire, soft and not easyto clog | Suitable for light, fragile or chemically sensitive materials, such as food, medicine, etc. |
 |
②Classification by aperture size
| Coarse screen |
 |
Coarse screen has a larger aperture (usually ≥2 mm) and is used to separate large particles | Suitable for preliminary screening, such as ore, building aggregate, etc. |
| Medium screen |
 |
Medium aperture (0.1 mm to 2 mm), used for routine particle size analysis | suitable for most granular materials, such as sand, powder, etc. |
| Fine sieve |
 |
smaller aperture (usually ≤ 0.1 mm), used to separate fine particles | suitable for fine powder or micro-particle materials, such as cement, flour, etc. |
③Classification by shape and number of layers
| Circular sieve |
 |
the sieve is round, often used in laboratories or small s creening e quipment | suitable for particle size analysis of s mall batches of samples |
| Square sieve |
 |
the sieve is square, often used in vibrating screening machines in industrial production | suitable for large-scale continuous s creening |
| Single-layer sieve |
 |
only one sieve, used for separation of a single particle size range | suitable for simple screening tasks |
| Multi-layer sieve |
 |
multiple sieves are superimposed, used to separate multiple particle size ranges at the same time | suitable for comprehensive particle size analysis, such as particle size distribution test |
| No. | Technical | Technical indicate | |
| 1 | Sieve Diameter | 200mm 8inch/300mm 12inch 450mm 18inch/100mm 4inch/75mm 3inch | |
| 2 | Material | Stainless steel or Brass | |
| 3 | Inner height | 50mm and 60mm | |
| 4 | Aperture size range | 0.02mm to 125mm | |
| 5 | Hole model | Wire mesh and perforated plate | |
| 6 | Detail aperture | 125, 106, 100, 90, 75, 63, 53, 50, 45, 37.5, 31.5, 25, 22.4, 19, 16, 13.2, 12.5, 11.2, 9.5, 8, 6.7, 6.3, 5.6, 4.75, 4, 3.35, 2.8, 2.36, 2, 1.7, 1.4, 1.18, 1, 0.85, 0.71, 0.6, 0.5, 0.425, 0.355, 0.3, 0.25, 0.212, 0.18, 0.15, 0.125, 0.106, 0.09, 0.075, 0.063, 0.053, 0.045, 0.038mm etc. | |
| 7 | Use | Grading Standard Testing Sieve Test Sieve for soil test sieve, aggregate sieve, concrete test sieve, cement test sieve, asphalt test sieve, wet sieve, wire mesh sieve, perforated sieve, astm sieve, en sieve |
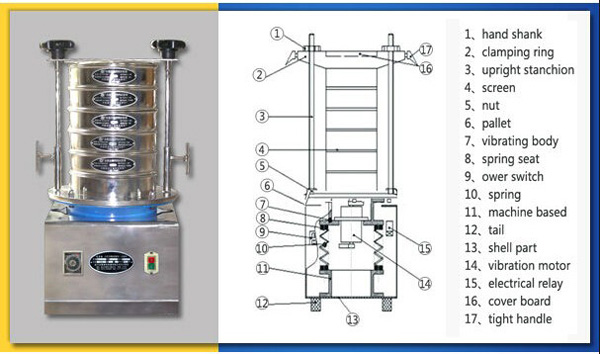
A test sieve consists of a set of sieves with different aperture sizes, arranged from largest to smallest. Its simple structure and easy operation allow for a direct visual display of the distribution of materials at different particle size levels, making it a benchmark tool for particle size analysis.
A sieving machine, on the other hand, is a complementary mechanical device that replaces manual operation with uniform vibration or tapping. It effectively ensures that materials are fully dispersed on the sieve surface, improving sieving efficiency and accuracy while reducing the workload of laboratory personnel.
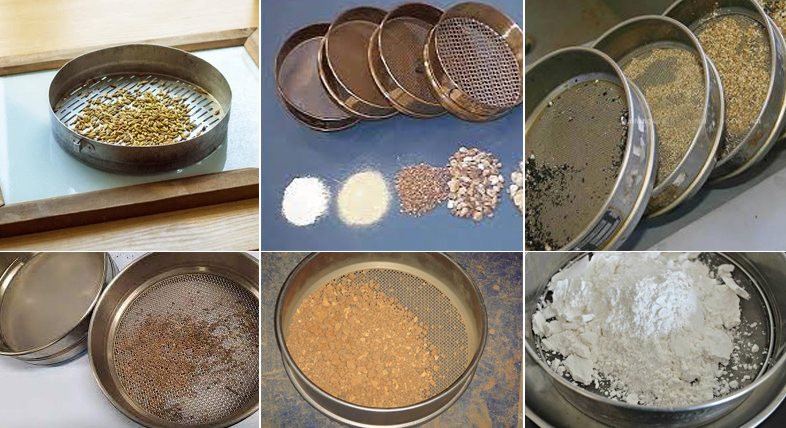

Sieve analysis is a versatile and widely used technology with numerous applications across various industries. By accurately determining the particle size distribution of materials, sieve analysis plays a crucial role in quality control, process optimization, and scientific research. For example, in fields such as building materials and chemicals, it is used to monitor the particle size of crushed and ground products to optimize processes, assess the suitability of raw materials such as cement and ceramic powders, and ensure the processing quality of products such as fertilizers and feed.
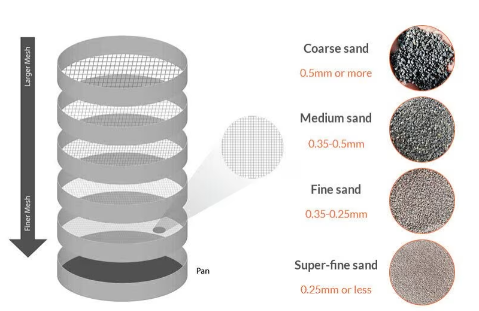
Steps:A sample of the material to be tested is collected and placed on a set of stacked sieves with progressively finer mesh sizes.The sieves are then mechanically shaken or vibrated for a specific amount of time to separate particles based on size.
Particle Separation:As the material is shaken, particles smaller than the sieve openings pass through to the sieve below, while larger particles are retained on each sieve.Each sieve retains a specific range of particle sizes.

Measurement:After the shaking process is complete, the amount of material retained on each sieve is measured.

The results of the sieve analysis are used to create a particle size distribution curve, which shows the percentage of material passing through each sieve size.
Overall, sieve analysis is a fundamental technique in material testing and characterization, providing valuable information about the particle size distribution of granular materials, which is essential for various engineering and construction applications.

Sieve analysis is generally suitable for spherical or near-spherical particles, but may not be accurate enough for irregularly shaped particles; sieve analysis has relatively low precision and cannot provide accurate particle size data, especially when the particle size distribution is narrow or the particle shape is irregular; sieve analysis may not be effective in detecting very fine particles, as these particles may pass through the sieve openings and be missed; to obtain more accurate results, multiple sieves and repeated experiments are sometimes required, which increases the time and labor costs of the experiment.

Five Advantages of Rotap Sieve Shaker
Rotap Sieve Shaker is mainly composed of machine base, sieve and transmission mechanism. It can be equipped with special fixtures, which can be used to clamp 200 test sieves, as wel...
Slap Type Test Sieve is mainly used in laboratories within universities/research institutes/enterprises, with standard test sieves for particle size analysis and detection of granul...
Soil sieve analysis is a soil particle size determination method based on the principle of mechanical separation...
Juice Powder Ultrasonic Sieve test
The ultrasonic sieve test for juice powder is a fine screening equipment designed for delicate, moisture-absorbing...
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils
Standard Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils (ASTM D422)aims to accurately determine the size distribution of soil particles...
Size sieve for soil primarily involves the sieve frame diameter and sieve aperture size...
Laboratory woven wire mesh sieves
Laboratory woven wire mesh sieves are screening tools made of 250 mm stainless steel frame and precision woven wire mesh. The high quality of the equipment ensures reliable screenin...
Sieve Mesh is a metal or non-metal device used to separate materials. Its mesh count refers to the number of holes per square inch. It sorts powders by particle size through vibrati...
For Laboratory Sieves Price ranges from $100 to $500 USD, and the price varies depending on the sieve diameter, mesh range, material, and quantity.......
For Laboratory Sieves Suppliers
For Laboratory Sieves Suppliers manufactures sieve frames in 3-inch, 8-inch, and 12-inch diameter sizes, including perforated plate screens, wet-washed screens, and woven wire mesh ...
Are you interested?
![]()
Then we look forward to hearing from you
Contact Us
Industrials
Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road sitemap
