Friday May-16 2025 16:32:30
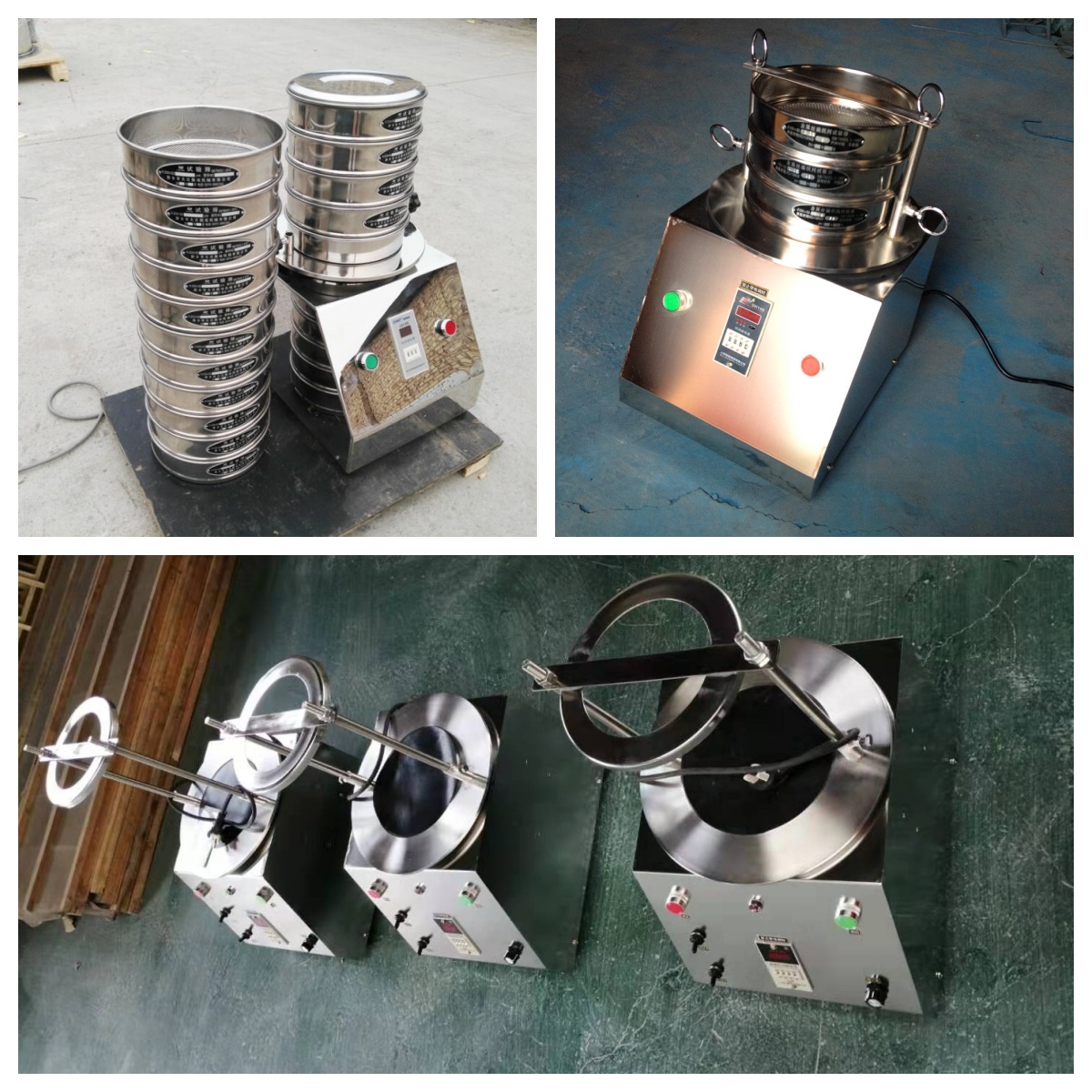

The test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil (sieving method) is an important method for determining the particle size distribution of soil in geotechnical tests. It is mainly used to determine the distribution of particles of different particle sizes in fine-grained soil (such as clay and silt), and is suitable for soil with a particle size greater than 0.074mm, which is crucial for soil classification and engineering property evaluation.

The purpose of test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil(screening method) is to determine the particle size distribution of fine-grained soil by screening method, analyze the composition and size distribution of soil particles, and provide a basis for soil classification, engineering property evaluation, and application in agriculture, environment and other fields. Specifically include:
Determine the soil type (such as sandy soil, silt soil).
Evaluate the physical properties of soil, such as permeability and compressibility.
Provide data support for engineering design, soil fertility research or pollutant migration analysis.
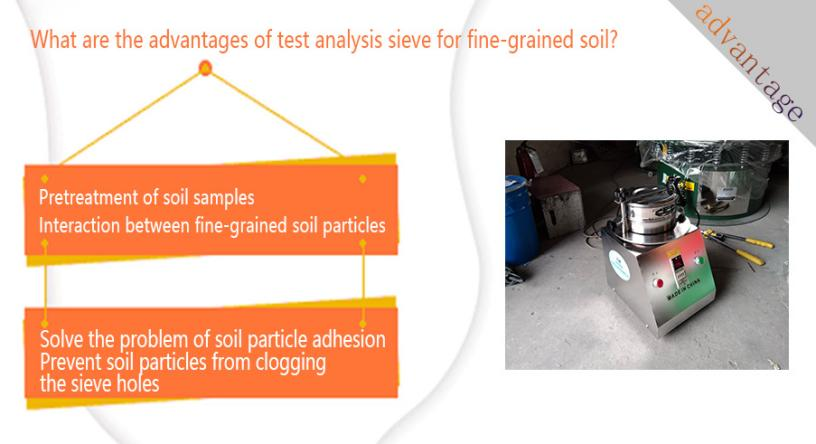
Pretreatment of soil samples: Pretreatment of fine-grained soil samples before screening, such as crushing, grinding, etc., to reduce the particle size of soil particles, make it easier for soil particles to pass through the sieve holes, and reduce the probability of sieve hole blockage. At the same time, the soil samples can also be treated by desludging, dehydration, etc. to reduce the sticky substances and moisture in the soil samples and improve the screening effect.
Interaction between fine-grained soil particles: Fine-grained soil particles may agglomerate during screening, affecting the screening effect. Adjust the screening time and vibration frequency to adapt to the characteristics of fine-grained soil. The test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil adopts multi-stage screening technology to gradually separate particles of different particle sizes.
Solve the problem of soil particle adhesion: For fine-grained soil, dry screening or wet screening can be selected according to its characteristics. Dry screening is suitable for fine-grained soil with low water content. First, the soil sample is dried to reduce the moisture between soil particles and reduce viscosity before screening. Wet screening is to use the test sieve to screen directly in water, using the lubrication and dispersion effect of water to reduce the adhesion between soil particles, so that fine-grained soil can be more easily dispersed and pass through the sieve holes.
Prevent soil particles from clogging the sieve holes: Keep the sieve in a tensioned state to prevent the sieve from being relaxed during the screening process and avoid clogging the sieve holes due to deformation of the sieve. The tensioned sieve can better withstand the impact and friction of fine-grained soil and reduce the possibility of soil particles getting stuck in the sieve holes. Equipped with an automatic cleaning device or regular manual cleaning of the sieve to remove soil particles adhering to the sieve.

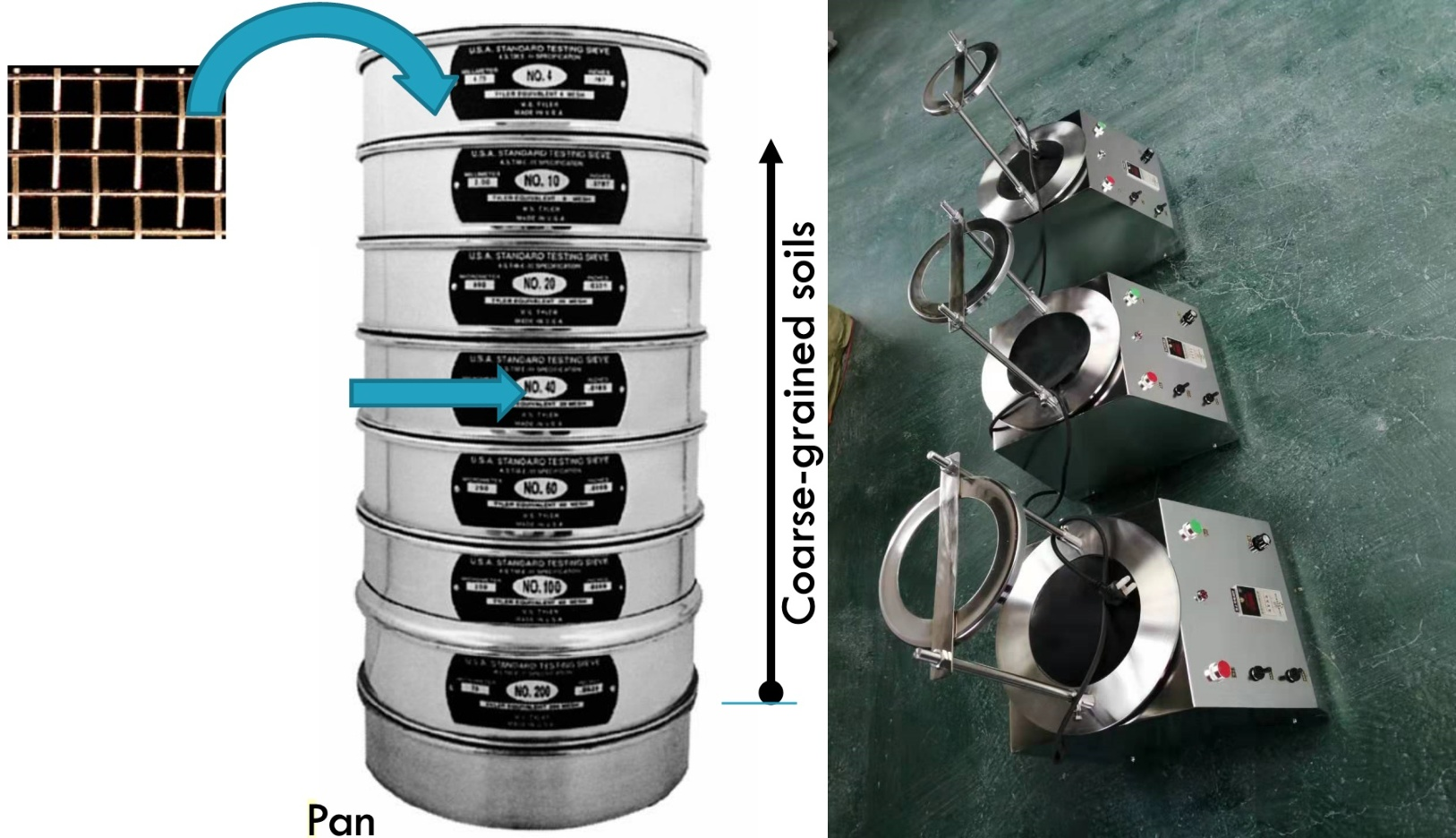
The mesh number of test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil is directly related to the sieve hole diameter. Its core purpose is to separate soil particles through sieves of different mesh numbers and then analyze the particle size distribution. It is usually selected according to the particle size that needs to be screened. Common mesh numbers include:
200 mesh (about 75 microns): used for screening fine-grained soil, such as clay and silt.
100 mesh (about 150 microns): screens finer particles, suitable for fine sand and fine-grained soil.
60 mesh (about 250 microns): used for screening medium-fine soil, often used for soil classification.
|
Mesh number (mesh) |
aperture (mm) |
applicable instructions |
|
10 mesh |
2.00 mm |
coarse particle primary screen, non-fine particle main screen |
|
20 mesh |
0.85 mm |
transition screen |
|
40 mesh |
0.425 mm |
commonly used for silt screening |
|
60 mesh |
0.25 mm |
fine silt and sand boundary screen |
|
100 mesh |
0.15 mm |
commonly used in silt/clay transition zone |
|
200 mesh |
0.075 mm |
fine grain boundary standard screen (commonly used) |
|
300 mesh |
0.050 mm |
used for finer particle detection (precision screen) |
|
400 mesh |
0.038 mm |
ultrafine particle detection, often used in scientific research or high-demand tests |
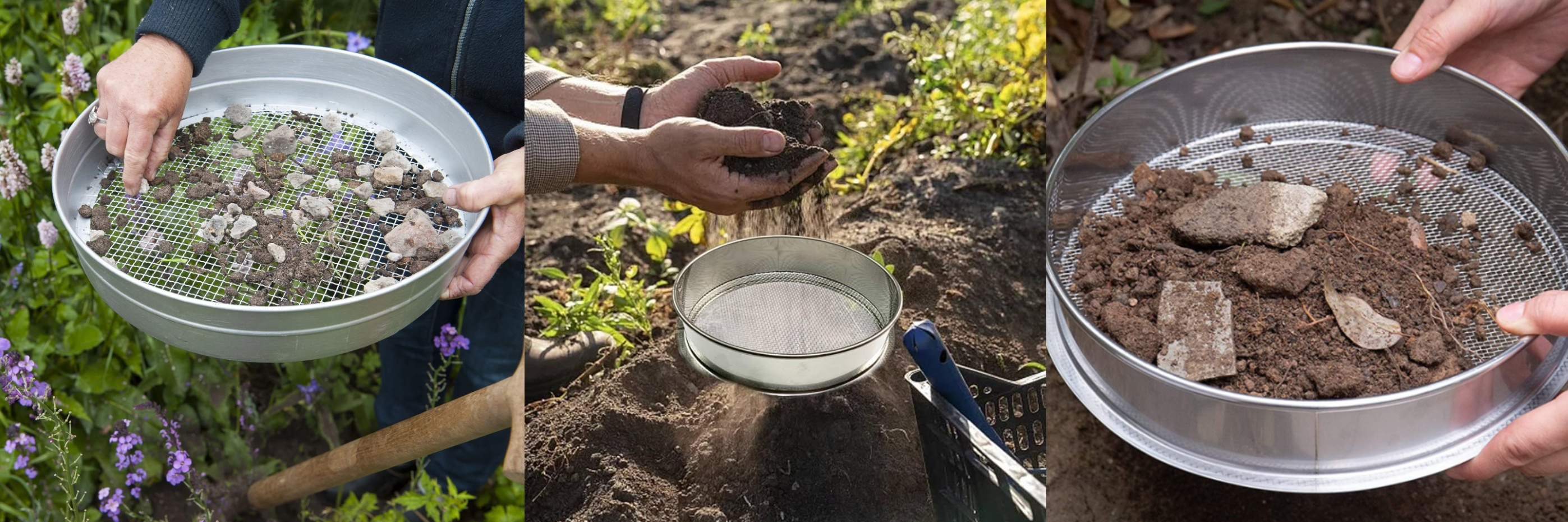

The main purpose of test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil is to analyze the distribution of soil particle size, that is, soil particle size analysis. It classifies soil samples through sieves of different apertures, determines the content of soil particles in each particle size range, and thus determines the particle size composition of the soil. This is crucial for the following aspects:
Soil classification: Particle size analysis results are the basis for soil classification, such as sand, clay, silt, etc. (<0.075mm) soil fine particles.
Engineering property evaluation: Understanding soil particle size distribution (gradation) helps to evaluate the mechanical properties of soil, such as permeability, compressibility, bearing capacity, etc., and guide foundation design and construction.
Agricultural and environmental research: Particle size distribution affects soil water retention, fertility and pollutant migration characteristics, and is used for agricultural improvement and environmental monitoring.
Geological and hydrological research: Laboratory comparative tests and original soil sample analysis, analyzing the particle size of fine-grained soil helps to study sedimentation processes, water flow characteristics and erosion potential.
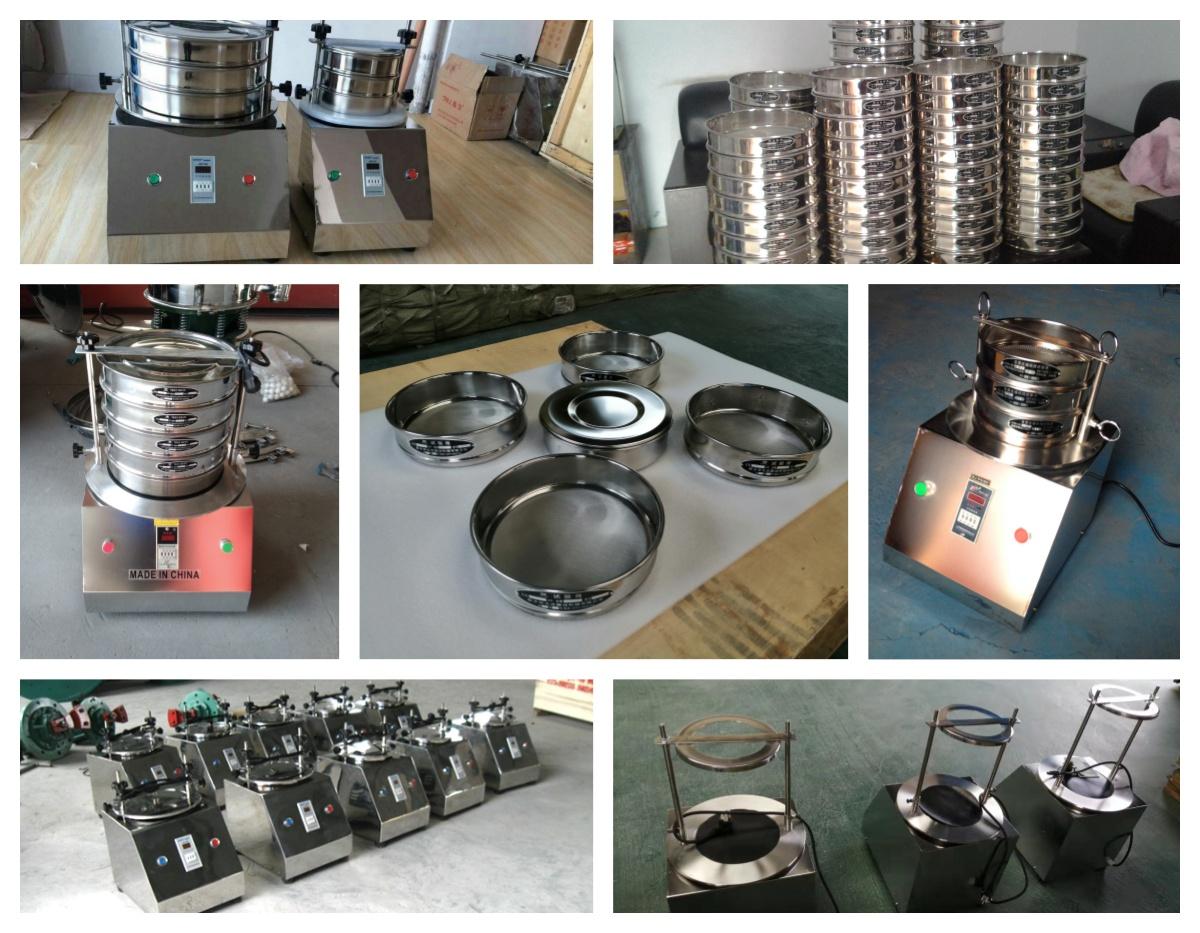

Test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil is an important tool for analyzing the particle size distribution of fine-grained soil in geotechnical tests. It separates soil samples into components of different particle sizes through a series of standard sieves with different apertures, and then calculates the percentage of particles of different particle sizes by weighing the mass of each component, which is finally used to draw particle gradation curves and provide basic data for soil classification, engineering property evaluation and other related research and applications.
What is the wet sieving process?
Wet sieving process is a sieving process assisted by a liquid (usually water or a solution containing a dispersant) to more effectively...
Fines content tester can be defined as an instrument used to quantitatively determine the content of fines powder components of a specific fineness...
Micro silica powder particle size analysis test sieve
Micro silica powder, also known as silica fume, is an ultrafine active silica material with a very small particle size, usually between 0.1-0.3 microns, which...
Agricultural gruesos Test sieves
Agricultural gruesos test sieves are experimental equipment used for particle size analysis, grading and testing of agricultural soil, gruesos...
Stainless steel frame and woven cloth
The test sieve is a laboratory equipment used for particle size analysis. Its core components usually include a stainless steel frame and woven cloth (also called a sieve)...
Test Analysis sieves For Fine-Grained Soil
The test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil (sieving method) is an important method for determining the particle size distribution of soil in geotechnical tests. It is...
May 16, 2025
Test Analysis sieves For Fine-Grained Soil
The test analysis sieve for fine-grained soil is a key tool for determining the particle size distrib...
May 15, 2025
Test sieve for flour quality control
The test sieve is an indispensable key screening equipment in flour quality control. It can grade and...
May 14, 2025
test sieve for aggregate particle size
The test sieve for aggregate particle size is a standard sieve used to evaluate the particle size dis...
May 13, 2025
Test sieve for pharmaceutical powder
Test sieve for pharmaceutical powder is a special equipment used in the pharmaceutical industry for a...
![]()
Then we look forward to hearing from you
Contact Us
Industrials
Yanjin county forest park gate to the west 1000 meters north road sitemap
